Introduction
Laparoscopic scissors are specialized surgical instruments designed for cutting tissues during minimally invasive (laparoscopic) procedures. They are inserted through small incisions using trocars and allow surgeons to cut with precision inside the abdominal cavity without needing a large open incision. Their design promotes minimal tissue trauma, faster healing, and reduced post-operative complications, making them essential in modern surgical practices.
Design and Structure
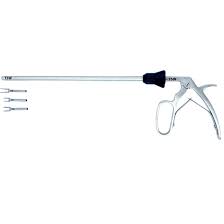
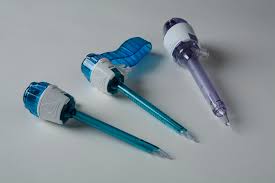
Laparoscopic scissors are composed of three main components: the handle, shaft, and scissor blades. The handle is ergonomically designed, often with a ratcheting mechanism or spring-loaded action for comfortable, precise operation. The long, narrow shaft enables access to deep-seated structures through trocars, typically ranging from 5mm to 10mm in diameter.
The blades at the tip come in various shapes, such as straight, curved, or angled, and are typically made from high-quality stainless steel. Some scissors are coated or insulated for use with electrosurgical units, allowing simultaneous cutting and coagulation of tissues.
Types of Laparoscopic Scissors
Several types of laparoscopic scissors are available to suit different surgical needs:
-
Straight Scissors: Ideal for precise linear cuts in soft tissues.
-
Curved Scissors: Allow better access around anatomical curves or structures.
-
Hook Scissors: Designed for sharp dissection and separating tissues.
-
Monopolar Scissors: Equipped with an insulated shaft for use with electrosurgical generators to cut and coagulate simultaneously.
-
Metzenbaum Scissors: Longer blades for delicate dissection and tissue cutting.
The selection of scissor type depends on the procedure, surgeon preference, and tissue type involved.
Surgical Applications
Laparoscopic scissors are used in various surgical procedures including:
-
Cholecystectomy – for cutting the cystic duct and artery.
-
Hernia repair – for tissue dissection and mesh trimming.
-
Gynecological procedures – such as hysterectomy and tubal ligation.
-
Colorectal surgeries – for dissection and bowel mobilization.
Their sharp, fine blades offer precision and control, essential for safe and effective tissue management.
Sterilization and Maintenance
Reusable laparoscopic scissors must be properly cleaned, sterilized, and inspected before and after each use. Most are autoclavable, ensuring high levels of infection control. Proper maintenance, including regular blade sharpening or tip alignment, ensures the longevity and performance of the instruments. Disposable variants are also available for single-use applications, offering convenience and reduced risk of cross-contamination.
Conclusion
Laparoscopic scissors are indispensable tools in minimally invasive surgery, enabling precise tissue cutting while minimizing patient trauma. Available in various configurations to meet diverse surgical needs, these instruments contribute significantly to surgical efficiency, accuracy, and patient recovery. Their role in enhancing the safety and effectiveness of laparoscopic procedures makes them a fundamental component of the surgical toolkit.




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.